What is The Best Silicon Wafer For The Etching Processes?
Questions Regarding Silicon Etching
If you need an etching solution, we have it!
- Buffered Oxide Etching
- Copper & Gold, and Etching
- KOH Etching
- Piranha Etching
- Silicon Nitride Etching
Get Your Quote FAST!
Wafer Etching Process
The silicon etching process consists of chemically reducing the silicon layer to a n-dimensional structure. In the first step, a sample is prepared by soaking the sample in a solution of a soluble acid. The solution is then lowered in temperature to a specific molten point. A series of tests are performed to examine the etch rate and the anisotropy, uniformity, and mask selectivity of the etched layer.
Wet Etch Process
Once the silicon trench etching process is complete, the wafers are transferred into an intermediate transfer chamber that contains carrier gas containing water vapor. In this step, chemisorbed bromine and residual HBr are removed from the wafers. The halogen removal is carried out in a separate chamber within the etching tool. In the transfer, the wafer is transferred without destroying the vacuum. The water vapor in the carrier gas is passed over the wafer.
Semiconductor Etching Process
To determine if the chemical reaction will work, a sample must be exposed to the etching solution. A thin film of silicon nitride is deposited directly on the silicon wafer. The nitride bath is an optimum temperature for the silicon nitride etchant. This bath regulates the ratio of water to acid. Be careful not to add too much water at once, as too much will cancel the boiling process and cause a dangerous explosive reaction.
Silicon Wafer Used for the Etching Processes
Silicon wafer etching processes are used for removing oxide layers from silicon micro-electronic devices. They are generally acidic and involve the exposure of a sample to the etching solution. The final product consists of a thin film of silicon nitride. To perform this process, the sample must be exposed to the etching solution at the correct temperature. The nitride bath is heated to the optimum temperature and a certain level of reactivity to regulate the ratio of acid to water. If the ratio of acid to water is too high, the boiling process will be canceled and a dangerous explosive reaction will occur.
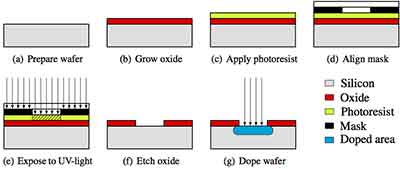 To perform this process, a high concentration of hydroxide ions is necessary. It is essential that the etchant contains a minimum of 15% hydroxide ion source. The etchant used in the process should contain at least 40 wt% water vapor. Some of the most common etchants contain as much as 65 wt% hydroxide ion source.
To perform this process, a high concentration of hydroxide ions is necessary. It is essential that the etchant contains a minimum of 15% hydroxide ion source. The etchant used in the process should contain at least 40 wt% water vapor. Some of the most common etchants contain as much as 65 wt% hydroxide ion source.
The next step is preparing the etching solution. It contains a concentration of phosphoric acid that is at least 180 c. This is used to complete the etching process. The nitride bath is used to maintain the correct balance of acid to water. Adding too much water is a major risk and can cancel out the etching process. It may even result in a chemical explosion.
Once the solution has been prepared, the process can begin. The first step involves agitating the etching solution. The next step is applying the etching chemicals to the silicon wafer. The agitation will ensure the atoms on the wafer are evenly distributed throughout the ion source. Afterwards, the silicon wafer will be etched. If the process is a bit complex, a qualified technician can answer your questions and ensure the process is done properly.
After the caustic etchant is applied, the silicon wafer is placed in the etching apparatus. This etchant can be either applied directly onto the silicon wafer or sprayed into the wafer. It is possible to combine the etchant and the silicon wafer in a wet bench. However, this is not always the case. It can be made to be a dry etching process.
The process requires a hydroxide ion solution, which is a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxide. The concentration of the etchant must be greater than 15% wt. Typical etchants have at least sixty-five percent hydrogen peroxide. This concentration is needed to remove the nickel. A wet etchant contains a chelating agent.
Polymer etchants are preferred for the etching process to minimize the risks of metal contamination to silicon wafers. When the etchant is fresh, the free metal ion concentrations should not be greater than one ppb. While this method is the most commonly used, it is also considered to be the most safe. The etchant should have a pH level of at least 12.
Various etchants are available. The most common etchants are based on the concentration of hydrogen ions and sodium hydroxide. The concentration of the etchant is important as it is essential to have a proper chemical composition for the etching process to be effective. For instance, the etchant should be high enough to dissolve the silicon layer. It must be strong enough to remove the etchant.
The silicon etching process is a chemical process that reduces the silicon layer to an n-dimensional structure. The sample is prepared by immersing the sample in an acidic solution and then lowered to a specific molten point. Once the sample is etched, a series of tests are performed to evaluate the etching rate, uniformity, and mask selectivity. The most important of these tests is the analysis of the etching process.
The etching process is an important part of semiconductor production. This process can be used to create a variety of different types of semiconductor devices. The etching process is an essential part of the semiconductor industry and enables high-speed manufacturing. It can also be used to create a range of products with low cost. It is widely used for a wide range of applications. It is also used in various industrial and research environments.
Best Silicon Wafer Etching Processes
Etching is a microfabrication process that differs depending on the use of the silicon wafer. For solar cells with too much glare, unwanted material can be etched off the wafer. Or some sidewalls may need to be increased vertically or smoothed out to obtain a desired pattern. Physical incising and chemical baths are the prime way to achieve this. To achieve a desired etching a dry or wet etching must take place. Dry etchings, sometimes referred to as “plasma” or “reactive-ion” etchings remove unwanted material by utilizing reactive chemicals, gases, beam-induction, plasma and physical bombardment. It may also be a combination of physical bombardment and chemical reactions. The most common method of etching is wet etching. This capitalizes on the wafer being immersed in a liquid solution. The solution’s goal is to remove layers of unwanted material from the silicon wafer while the protective layer remains intact. Silicon wafers may be etched isotropically and anisotropically as well. Isotropic etching will have the same etch rate in all directions and anisotropic etches will have different vertical and lateral rates. Silicon wafers can be purchased in various quantities online and some websites will offer prompt feedback on any etching concerns you may have.
Buffered Oxide Etching
Sometimes referred to as Buffered HF or BHF this wet etchant is used for thin films of Silicon and Silicon Dioxide that need to be etched. To achieve this, aluminum fluoride or another buffering agent as well as hydrofluoric acid must be in place. This allows for a repeatable process with consistent results. Buffered Oxide Etching is also photoresist compatible, won’t contaminate or stain silicon, and wont undercut masked oxide. Plasma etching can also be performed for BOE as it’s more precise and the elimination of hydrofluoric acid solutions make it much safer.
Copper & Gold, and Etching
To conduct electric signals, metallic connections must be developed on microelectronic devices. To achieve this, silicon wafers will have deposits of copper, gold, or aluminum as these materials are highly conductive. Metals will have to be etched during the silicon wafer process. This can be challenging, as each one requires different chemicals based on its process. However it is relatively safer as it doesn’t require the highest of temperatures. Most commonly, metal etching is performed in a vacuum to ensure hydrogen bubbles are instantly removed so snow and bridging reactions do not occur. A vacuum metal etcher will immediately pump and evacuate any hydrogen bubbles. For gold, a strong oxidiser is required for separating unpaired valence electrons and a complexing agent is needed for suppressing oxidised gold reassembly. Luckily, gold is more commonly used for contacts and protection and it has high chemical stability. Copper is more commonly used however for it’s low cost and high conductivity in microelectronics. A combination of electroplating and a wet-chemical method needs to be used however because it can’t be achieved through plasma dry-etching.
KOH Etching
For fabricating silicon nanostructures a wet Potassium Hydroxide wet etching process must be performed. It creates cavities in your silicon wafer and allows for optimal precision. DI water and thermal regulation is used with pH > 12 or another corrosive alkaline compound. Consistency through the nano chemical process will assure precision of the Si wafer etching as the etch rate is limited. However, since this process ensures optimization, it has become one of the most popular methods because it can be automated. This increases the efficiency of the etch and greatly reduces the cost. This also makes it prime for batch etches and is amongst the most safe.
Piranha Etching
Mixtures of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide are used in the piranha etching solution. This allows silicon wafers to be clean during the process of semiconductor manufacturing. This will ensure organic compounds found on substrates are cleaned and most metals will be oxidized. Photoresist can also be removed. However this process, although very effective, is not used often as it’s very dangerous. It uses highly corrosive and powerful oxidizers so great safety measures must be taken throughout. It should also never be stored and used immediately as it generates toxic gases. Safe disposal is also strongly encouraged.
Silicon Nitride Etching
In semiconductor manufacturing silicon nitride works as a masking material. A thin film of silicon nitride is placed directly on the silicon wafer and phosphoric acid is used to complete the etching. This is done in a nitride bath with a hot phosphoric acid strip at 180c and DI water. A bath of nitride will ensure temperature precision and the deionized water to phosphoric acid ratio will be regulated. Keep in mind that adding water to this solution can increase risk, as too much water at once will cancel the boiling and leave a film of water above the acid. This in turn will cause the acid to boil and an explosive reaction will occur. Only add small amounts of water at a time and make sure your silicon nitride etching environment is accurately controlled.
Never etch with chemicals you’re unsure about as it puts you and others at risk. Contact a certified professional on the matter and ensure you have all your questions about silicon wafers answered before you perform any etching process.
