Do you have some good fundamental materials data on silicon refractive index and optical absorption vs wavelength (and also effect of doping on these numbers). I have some data but actually found it difficult on the web to locate the motherlode for such information. It would also be really useful to me if you have similar data for GaAs material as this looks to be an equally good material to use as a high index etalon .. although I’m thinking its downside would be cost?
What is Silicon Refractive Index?
- Home
- About Us
- Substrates
- Silicon Wafer
- Silicon Wafer Diameters
- 25.4mm Silicon Wafer
- 50.8mm Silicon Wafer
- 76.2mm Silicon Wafer
- 100mm Silicon Wafer
- 125mm Silicon Wafer
- 150mm Silicon Wafer
- 200mm Silicon Wafer
- 300mm Silicon Wafer
- 450mm Silicon Wafers
- 1 Inch Silicon Wafer
- 2 Inch Silicon Wafer
- 3 Inch Silicon Wafer
- 4 Inch Silicon Wafer
- 5 Inch Silicon Wafer
- 6 Inch Silicon Wafers
- 12 Inch Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Types
- P-Type Silicon
- N-Type Silicon
- Undoped Silicon
- Float Zone
- Silicon Wafer Flats
- Single Side Polished Silicon Wafers
- Double Side Polished Silicon Wafers
- As-Cut Silicon Wafers
- Lapped Silicon Wafers
- Etched Silicon Wafers
- Low Total Thickness Variation Silicon Wafers
- Porous Silicon
- Thin Film
- Ultra-Flat Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Grades
- Silicon Wafer Mobility Calculator
- Soft Lithography
- PDMS Micro-fluidic Chip Platforms
- Platinized Silicon Wafer
- Epitaxial Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Surface Roughness
- Silicon Wafer Uses
- Semiconductor and Related Device Manufacturing
- Gold Coated Silicon Wafers
- X-ray diffraction @ zero background specimen holder
- Diced Silicon Wafers
- Wafer Bonding
- Wafer Preperation
- Wafer Processing
- Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Modified Silicon
- Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP)
- Silicon Wafer Microfluidics
- Thinnest Silicon Wafers
- Annual Volume of Silicon Wafer Production
- Plasma Etching Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Annealing
- Direct Radioactive Nuclide Electricity
- Polycrystalline Silicon
- Substrates 2d Materials
- Zinc Oxide on Silicon
- FTIR Undoped Silicon
- High-Pressure Synthesis Experiments
- Silicon Pillars
- PDMS Microstructures
- Silicon Mirros
- Ar Ion Evaporator Deposited Metal Contacts
- Silicon Ingots
- PTFE
- Silicon Wafer Sorting
- Black Silicon Wafers
- Ultra-Flat Silicon Wafers
- Diced Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Bonding
- Silicon Wafer Fabrication
- Cleaving Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Orientation
- Ultra-Thin Silicon Wafers
- Custom Silicon Wafers
- Silicon Wafer Suppliers
- Partical Count
- Silicon Wafer Diameters
- Aluminum
- Glass Wafers
- Fused Silica Wafers
- Gallium Nitride Wafers (GaN)
- Germanium Wafers
- Graphene
- Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- Sapphire (Al2O3) Wafers
- Quartz Single Crystal
- Solar Wafers
- TEOS Oxide
- Silicon on Insulator Wafers
- Thermal Oxide
- Silicon Wafer
- Blog
- Wafer Store
- Contact Us
What is Silicon Refractive Index?
A student asked the following question:
Click for Answer, or reference #253024 for specs and pricing.
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researchign today!
What is Silicon Refractive Index?
The silicon refractive index is 3.88163 and its extinction coefficient is 0.01896923.
How to Calculate Silicon's Refractive Index?
The Refractive Index (RI) is the number that describes the ability of a material to bend light. It is the ratio of the speed of light to its wavelength. Typically, RI values are in the range of one to two. There are materials, however, that have higher or lower RIs than water. Using the equation above, you can find the RI of different media. Let's look at a few examples.
The refractive index of a material is equal to its ratio of real and imaginary parts. The n is the observed speed of light in the medium. The k is the factor of total internal reflection. Setting the angle of incidence to 90 degrees allows you to calculate total internal reflection. Since the light can't be refracted by any angle greater than 90 degrees, it will always be reflected. This is how to find a material's RI.
Refractive index is a measurement of how much light is distorted when it passes through different materials. It is important to know the RI of any substance before using it in a project. You can find out the RI of any material by looking at the rays' angles when they travel through a material. This information is useful when analyzing optical properties and evaluating the quality of a product.
How to Calculate Refractive Index Video
Silicon Refractive Index Questions and Answers
Scientist asked for the following quote:
I'm looking for some small (undoped) double sided polished silicon plates (supplied as plates) with dimensions 1.4mm x 1.8mm x 200um thick. Tolerance on absolute thickness is +./-25um but parallelism of polishes faces is important and must be better than a wedge angle of 0.005deg. Looking for quotes initially for 50, 100pcs for prototypes, but also 1000pcs quote for production.
I do see some 200um thick material there. It looks to be Boron doped. To be honest, I may be able to use doped material, but I need some advice. I’m intending to use the plates as low finesse etalons, but where I can get enough modulation without having to apply any fancy coatings. To do this, I need the material to have the highest index possible and also for there to be negligible optical absorption in the material for wavelengths between 950nm and 1400nm where my light sources are.
I wonder what is the effect of doping on the refractive index, and optical absorption spectrum. Also, I wouldn’t want there to be a radical increase in the temperature dependence of the refractive index.
UniversityWafer, Inc. Answsered:
The requirement of wedge angle < 0.005º needs clarification. I presume that it refers to the 1.8mm dimension. This means TTV<1,800µm tan(0.005), LTTV(1.4×1.8mm)<0.157µm. That corresponds roughly to TTV<5µm on 4"Ø wafer, TTV<2.5µm on 3" wafers or TTV<1.25µm on 2"Ø wafer. So it is achievable with 4"Ø or 3"Ø or 2"Ø wafers although LTIR or LTTV can be measured automatically only on 3"Ø and 4"Ø wafers. 4"Ø wafer will yield about 1,600 of 1.5×1.8mm Chips, 3"Ø will yield 800 and 2"Ø will yield 400. Even one 2"Ø wafer can yield more than 200 of 1.8×1.5mm Chips plus 4 of 5×5mm Squares {plus also some number of 5×1.8 and 5×1.5mm Chips}. In the attachment there is a description of light transmission/absorption properties of Silicon. As shown in Fig. 1, between 950 and 1,000nm Silicon is opaque. Be it doped or undoped, it does not transmit these wavelengths of light. Between 1,200 and 1,400nm {and on to 5,000nm} undoped Silicon transmits light with zero absorption. In this region light absorption depends on doping. However, for Silicon with n-type resistivity >10 Ohmcm or p-type >20 Ohmcm, both CZ and FZ crystalized, the absorption is so small that it cannot be distinguished from that of intrinsic Silicon. Absorption depends on the number of free charge carriers so it is proportional to material conductivity (inverse of resistivity) and material thickness. In 1,200 to 5,000nm range, although absorption is nil, transmission in air is no more than 52%. That is because of the rather high refractive index of Silicon which causes light to be reflected at air/silicon interfaces This can be mitigated by applying anti-reflection coatings. In the 950-1,400nm range:
- Germanium is opaque
- Indium Arsenide (InAs) is opaque
- Materials such as Monocrystalline Quartz, Fused quartz, Calcium Flouride (CaF2), Barium Floruide (BaF2) are transparent
- Gallium Phosphide (GaP) is partially transparent
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) is opaque for wavelengths <910nm (absorption coefficient >200/cm) At 950nm undoped GaAs is essentially transparent (absorption coefficient <0.01/cm). From 950 to 1,300nm GaAs it becomes even more transparent (absorption coefficient dropping still further). Between 1,300 and 1,400nm, GaAs is perfectly transparent (absorption coefficient as close to 0 as can be measured). Thus Undoped GaAs is considered transparent in the 950-1,400nm range and used as optical windows in that wave length range.
Reference #253024 for specs and pricing.
What are Some Silicon Refractive Index Applications?
Silicon has a relatively high refractive index, and it is used to make lasers, and optical tools. The PL spectra were obtained by calculating the thickness of a single silicon slab under different strain conditions. For each operation, a photo was taken to document the results. Each operation resulted in different numbers on the graph, which correspond to the bandgap shift and the change in refractive index.
What Influences Silicon Refractive Index?
The silicon refractive index is influenced by several factors.
- First, the wavelength of light passes through the material.
- Secondly, the density of the light absorbed by the material is different at various temperatures.
- Third, the silicon refractive index depends on the doping level and the amount of doping.
For a semiconductor device, the n is determined by the tensile and compressive stress. In addition, the silicon refracting power is dependent on the element thickness and the shape of the crystal.
What is Solar Cells Refractive Index?
Optical properties of silicon are measured at 300K. Typical operating wavelengths for solar cells made of silicon are 400 to 1100 nm. For more detailed data, you can refer to Green 2008 or pvlighthouse, which provide data in text, graphical, or Excel spreadsheet format. In addition to this, pvlighthouse has an extensive database of the properties of different materials. The na and ns refractive indices are used to compare the performance of different materials.
Silicon-on-Insulator Refractive Index?
Transmission losses in W1 PCWs of SoS are below the light line. The data insets show propagation losses above the light line. Insets in Fig. 2 illustrate the group index profile versus wavelength for the W1 PCW in SoS. The transmission loss of SoS is lower than the absorption losses of C2Cl4. Its refracting properties are less than that of air and water.
To compare the differences in the n and k, we first considered the strain effect on the silicon refractive index. The silicon refractive index is sensitive to the temperature and film structure, and we used a high-pressure laser to induce a pressure of 3 mm. The peak temperature of the beam is around 950 °C. This is enough for this material to transmit light at a wavelength of 1.4 nm.
The temperature coefficient of silicon is positive, reducing the bandgap. Its refractive index increases as temperature increases. The wavelength-dependent phase-shift of silicon is the same as that of alumina. The silicon wavelength-refractive index is based on the difference between the two. The polarization of the beam can be shifted in any direction and can cause a reflection in the beam. Alumina resists heat, while alumina has a low-cost thermal resistance.
The absorption coefficient of silicon is a function of wavelength. Compared to other materials, its absorption at long wavelengths is sharper. The inverse of the absorption depth is the spectral depth. For a 1 um pixel, the light intensity of a 5 nm-pixel camera has been reduced to 36% of its original intensity. It is important to note that the silicon refractive index is a good measure of how transparent a material is to sunlight.
What is Silicon Bandgap?
The bandgap of silicon is 1.11 eV in a relaxed beam and 1.10 eV in a bent beam. When the same beam is bent, the bandgap of silicon is shifted by the applied strain. The result of this measurement can be used to predict the bandgap of different materials. The refractive index of silicon is the most important factor in the optical properties of a material.
The PL spectra can be used to estimate the bandgaps of strained silicon. The calculated strain-bandgap relation for "bent1" is 0.61%, while for "bent2" and "bent3" beams, the calculated strain is 1.75% and 2.15% respectively. As for a 3D FDTD simulation, the corresponding data was simulated for a silicon crystal of the same size.
What is Silicon Carbide Refractive Index?
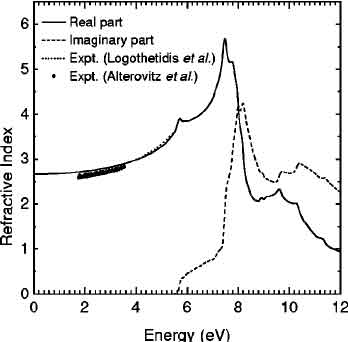 Silicon carbide is a semiconductor that is high in refraction and has excellent thermal conductivity. It also has low tensile and compressive stress. Its refracting power is determined by its crystal shape and thickness. The refractive index of SoS is about 1.3, which is very high. The refracting power is typically measured at 300K. In astronomical applications, it is used in solar cells. It is also used in spacecraft.
Silicon carbide is a semiconductor that is high in refraction and has excellent thermal conductivity. It also has low tensile and compressive stress. Its refracting power is determined by its crystal shape and thickness. The refractive index of SoS is about 1.3, which is very high. The refracting power is typically measured at 300K. In astronomical applications, it is used in solar cells. It is also used in spacecraft.
The ordinary refractive index of silicon carbide is 2.530 at 0.51 eV and increases to 0.336 eV at 3.69 eV. The transmission interference fringes of thin plates are used to normalize the dispersion curve, and this gives a low-frequency dielectric constant of 9.8. It is unclear how these data were obtained and why there is some disagreement. However, it is not impossible to determine the refractive index of silicon carbide.
The ordinary refractive index of silicon carbide is 2.43 at 0.51 eV and 0.336 at 3.69 eV. The interband index of 6H SiC is assessed and it goes from 2.530 to 2.868 at 3.69 eV. The inter-band index of the compound is evaluated by taking the transmission interference fringes as a reference. A low-frequency dielectric constant of 9.8 is obtained by extrapolating the high-frequency index of a thin-plate.
The Refractive Index of PDMS
PDMS is an optically transparent polymer that has a refractive index that matches the water's. PDMS 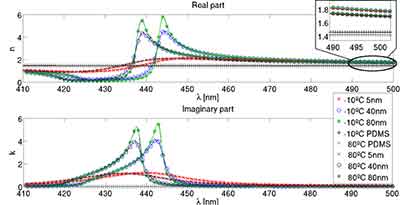 phantoms are typically cured so that they are more deformable and easier to transport. They are also in range of tissue refractive indexes. In this article, we will discuss the absorption properties of PDMS. In the context of spectroscopy, PDMS has a relatively low refractive indices, which makes it suitable for detecting the light reflected from the material.
phantoms are typically cured so that they are more deformable and easier to transport. They are also in range of tissue refractive indexes. In this article, we will discuss the absorption properties of PDMS. In the context of spectroscopy, PDMS has a relatively low refractive indices, which makes it suitable for detecting the light reflected from the material.
PDMS is typically coated onto the cladding of fibers to improve the transmission of evanescent waves. A core off-set fiber, a tapered fiber, or a bend fibre is a good candidate for this coating. These fibers exhibit high plasticity and are inexpensive. PDMS is especially advantageous for use in thermocouples, where the increased temperature sensitivity is crucial for detection.
PDMS is a versatile material. It can be deposited onto fibers and used to improve thermosensitivity and elasticity. Its high refractive index can make it ideal for optical components. The material is also useful for sensors. The PDMS membrane is used in the construction of temperature probes and acoustic waveguide. The PDMS-coated fibers are extremely durable, and the technology behind them is rapidly becoming more affordable.
The refractive index of PDMS relates to the path of light when it enters a material. It varies with the wavelength and is a key factor in total internal reflection. A polymer's refractive index determines the amount of light that is reflected at its interface. It also affects the intensity of the light reflected. It is essential to understand the process involved in determining the rays of a substance.
What Are the Optical Properties of Silicon?
The optical properties of silicon are best understood in terms of wavelength. This material has an absorption coefficient of cm-1 for visible light, and an inverse absorption coefficient for long-wavelength radiation. Generally, solar cells made of silicon operate between 400 nm and 1100 nm. For more detailed information, you can also refer to Green 2008. You can also consult pvlighthouse.com, which offers data in both graphical and text formats.
Optical constants are fundamental inputs for RT models, and the previously published values are not representative of the bulk physical properties of cubic SiC, the polytype that forms around carbon stars. The new SiC optical constants were derived from single-crystal reflectance spectra, and the authors explored the differences between a- and b-SiC and the weak features at the edges of the band.
One recent study has uncovered that a single-crystal SiC has a transmission loss of 1.5 cm-1 at 600degC and 1.4 cm-1 at 1000degC. The data show that this reduction is significant enough to suggest a route to the fabrication of compact, high-gain planar light sources and amplifiers. These results will allow us to design solar cells that are capable of generating a significant amount of electricity without any losses.
The new data on SiC optical constants will be fundamental inputs for RT models. The previously published values contain errors and do not reflect the bulk physical properties of cubic SiC, which is found around carbon stars. The new data are based on single-crystal reflectance spectra and investigate the differences between a- and b-SiC and weak features in the l 12.5-13 m region.
The new data on SiC reflectance spectra were previously published in the literature. However, these values were not accurate enough to reflect the bulk physical properties of cubic SiC, which is a cubic polytype found around carbon stars. The new data are derived from single-crystal reflectance spectra and investigate differences between a- and b-SiC, and weak features in the l 12.5-13 m region.
The new data also show that the new SiC optical constants have been derived from single-crystal reflectance spectra. They are more accurate than previously published values, which are based on bulk measurements of cubic SiC. The new value has been derived from a single-crystal reflectance spectrace. The data show that the a-SiC optical constants are slightly higher than the b-SiC values.
Since the a-SiC optical constants were determined, they were the fundamental inputs in RT models. But previously published data contained errors and did not accurately reflect the bulk physical properties of cubic SiC, which is found around carbon stars. The new values were derived from single-crystal reflectance spectra. The new results provide information on the differences between a-SiC and b-SiC, and the weak features of a-SiC.
Using a-SiC as an optical window, it can trap light in the 3 to 5 micron band. Similarly, it can be used as a substrate for optical filters. The use of this material is limitless. Large blocks of polished silicon are used as neutron targets for Physics experiments. This article explains the optical properties of this material. This substance is a great example of a semiconductor with many uses.
The a-SiC optical constants are fundamental inputs for RT models. The previously published values for these values are inaccurate and do not accurately reflect the bulk physical properties of cubic SiC. The new data are based on the sputtered silicon dioxide in an O2/Ar gas mixture. The concentration of the oxygen in the mixture determines the stoichimetric characteristics of the film.
The optical absorption spectrum of a nanocrystalline semiconductor can be determined from the band-gap energy of the material. The band-gap energy of a nanocrystalline semiconductor is estimated from the peaks in its optical spectrum. The frequency ranges of the emission spectra of a material are highly sensitive to its temperature. It is also useful for studying the band-gap of a particular material.
How to Obtain Optical Property Video
What is the Refractive Index of Silicon Carbide?
The refractive index of silicon carbide is 2.6353.
The refractive index of silicon carbide is an important parameter for solar panels. In the past, researchers have been able to calculate the value of the a-SiC optical constants using measurements of the polytypes. In this article, we provide new data based on sputtered samples of cubic SiC in O2/Ar gas mixture. This study provides the first reliable value of the a-SiC refractive index.
The ordinary refractive index of silicon carbide is 2.530 at 0.51 eV and rises to 0.336 at 3.69 ![]() eV. This material also has a low dielectric constant (as measured by transmission interference fringes), and is an excellent choice for high-end solar cells. The material is a popular material for spacecraft because it has low refraction. As an optical component, silicon carbide is very useful in space.
eV. This material also has a low dielectric constant (as measured by transmission interference fringes), and is an excellent choice for high-end solar cells. The material is a popular material for spacecraft because it has low refraction. As an optical component, silicon carbide is very useful in space.
The refracting power of silicon carbide depends on its shape and thickness. Its ordinary refractive index is 2.43 at 0.51 eV and 0.336 at 3.69 eV. The interband index for 6H SiC varies from 2.530 to 2.868 at 3.69 eV. The material's low-frequency dielectric constant is 9.8. The material's refractive index is a good indicator of its thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties.
The refractive index of silicon carbide is 2.6353, and its extinction coefficient is 0°. This means that silicon carbide is not a material to be used in lasers, but could be an indispensable material in other devices. A wide range of applications is anticipated for silicon carbide in the future. Its use in semiconductor electronics is expected to continue growing in the next several years. It is already used in radiation detectors.
